In recent years, the exponential growth of solar photovoltaic (PV) and wind energy has transformed the landscape of global energy production. Data from the International Energy Agency (IEA) reveals that from 2018 to 2023, the worldwide capacity for these renewable sources has more than doubled, marking a pivotal point in the world’s commitment to clean energy. This surge is largely attributed to favorable government policies and the steady decline in costs associated with renewable technologies. However, while the numbers reflect progress, they also highlight a pressing need for effective integration into existing power systems to fully harness these resources and mitigate potential drawbacks.
Solar and wind power are not merely trends; they embody essential strategies for decarbonization, particularly within the electricity sector. As two-thirds of the reductions in carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions required for achieving net-zero targets by mid-century will stem from these technologies, their effective integration is crucial. The IEA’s report underscores the potential risk of a disconnected energy grid, where the benefits of increasing renewable sources are lost unless cohesive integration strategies are implemented. Delays in these measures may lead to a significant reduction in the efficiency of power generation from solar and wind by as much as 15% by 2030.
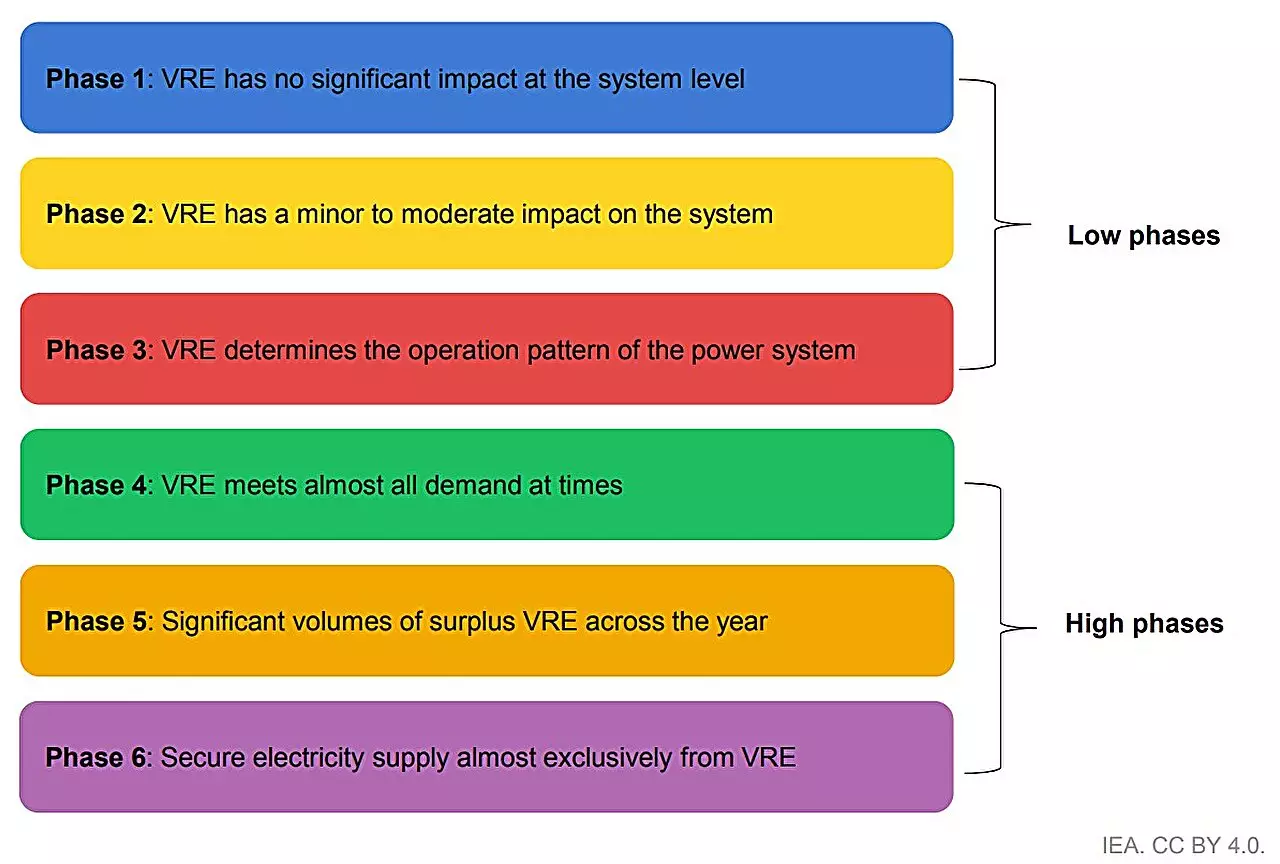
While the prospect of integrating massive amounts of solar and wind energy into power systems is a natural progression for many countries, it is not without its challenges. Varying grid capabilities across regions, differences in regulatory environments, and the inherent variability of renewable energy generation present substantial hurdles. The IEA’s report provides a comprehensive examination of these issues, presenting a global stocktake of integration practices across several key power systems that collectively produce nearly 90% of global solar PV and wind energy.
Effective integration requires an understanding of how to navigate these disparities in existing systems. Countries with lower shares of variable renewable energy currently have the opportunity to expand their generation without radical system overhauls. By employing proven methodologies, such as enhancing the flexibility of existing assets and employing advanced forecasting techniques, utilities can adapt to changing energy demands in a controlled manner.
The report highlights frontrunner regions such as Denmark, Ireland, South Australia, and Spain, which have successfully navigated the complexities associated with higher shares of renewable energy. These areas have not only invested in developing storage solutions and advanced grid technologies but have also established frameworks that allow them to manage fluctuations in energy production effectively. Critical to their success is a commitment to continuous improvement and iterative learning—recognizing that challenges will evolve as penetration rates increase.
Furthermore, these pioneering systems are showcasing how policy and regulatory frameworks can facilitate the integration of renewables without necessitating groundbreaking new technologies. Most of the technological solutions available are either mature or nearing maturity, suggesting that the focus should shift towards appropriate application and policy adoption rather than waiting for revolutionary advancements.
Looking ahead, it is clear that an urgent shift in strategy is required to integrate renewable energy more profoundly into power systems worldwide. As the pace of renewable adoption accelerates, policymakers must prioritize proactive measures that address the specific needs of their energy markets. This requires a paradigm shift in how energy systems are planned and operated, incorporating advanced predictive models and responsive measures that account for the unique characteristics of variable renewable energy generation.
While the current trajectory of solar PV and wind energy growth is promising, seizing the full spectrum of benefits hinges on effective integration strategies. Governments and energy stakeholders must act decisively, capitalizing on existing technology and enhancing grid flexibility to transition towards a sustainable and resilient energy future. The IEA’s insights serve as a vital roadmap for overcoming integration challenges and ensuring that the global transition to clean energy is both smooth and successful.

Leave a Reply