The quest for efficient indoor heating methods has long been a concern in both residential and commercial settings. As energy costs continue to rise and environmental concerns take center stage, the need for innovative solutions becomes more pressing. A recent study published in the journal Engineering outlines a groundbreaking development in heating technology: a novel radiant-convective heating terminal designed for intermittent heating. This advancement not only addresses the limitations of conventional heating systems but also paves the way for enhanced energy efficiency and thermal comfort in indoor environments.
Traditional heating methods often rely solely on radiant or convective systems, both of which have inherent disadvantages. For instance, radiant heating provides warmth through direct heat emitted from surfaces, while convective systems circulate warmed air. Each method, while effective in its own right, tends to falter when it comes to providing a stable and comfortable thermal environment during intermittent use. The need for a heating solution that combines these principles effectively is evident, particularly for low-demand heating scenarios common in residential settings. The existing systems often fail to heat spaces quickly enough or maintain desired temperatures comfortably.
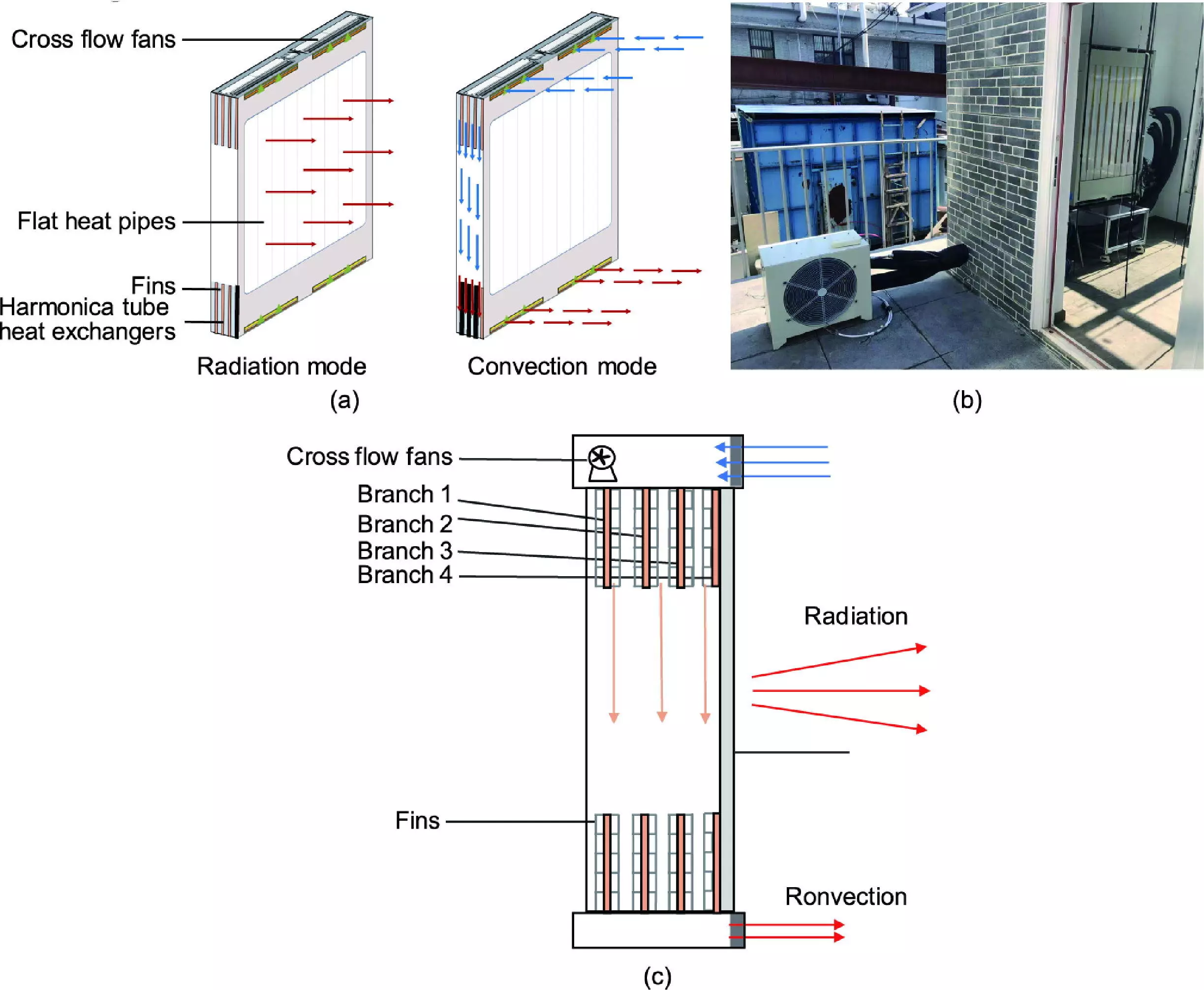
The study presents a revolutionary solution: a switchable radiant-convective heating terminal that combines the strengths of both systems. Researchers conducted experiments that evidenced this terminal’s capability to raise the temperature in typical residential spaces within a mere 20 to 40 minutes. Once achieved, it maintained a desirable temperature range of 18 to 22 degrees Celsius, demonstrating superior performance compared to traditional heating terminals. This innovation not only fosters rapid heating but also guarantees a comfortable thermal state, thus satisfying users’ dual desires for speed and comfort.
One of the significant findings of this research is the heating terminal’s adaptability and responsiveness. The switchable mode allows for quick transitions between heating styles, making it ideal for low-heating-load conditions often encountered in modern homes. By analyzing indoor environmental characteristics using both experimental and numerical simulation methods, the researchers have provided valuable insights into optimizing terminal heat transfer design. The implications of these findings extend beyond mere heating performance; they also touch on considerations for energy savings and system simplicity.
This exciting development offers a promising avenue for replacing multiple conventional heating systems with a single, efficient terminal. Not only does this result in cost savings for homeowners, but it also simplifies installation and maintenance, streamlining the overall heating strategy. By advocating for the adoption of this novel technology, the study not only enhances understanding of thermal environments but also lays the groundwork for future innovations in heating technology. In a world increasingly attentive to energy efficiency and environmental sustainability, advancements such as these could significantly mitigate heating-related carbon footprints.
The new radiant-convective terminal represents a significant step forward in the quest for efficient and comfortable heating solutions. As society’s demand for sustainable living increases, innovations like this will play a crucial role in shaping the future of indoor climate control.

Leave a Reply