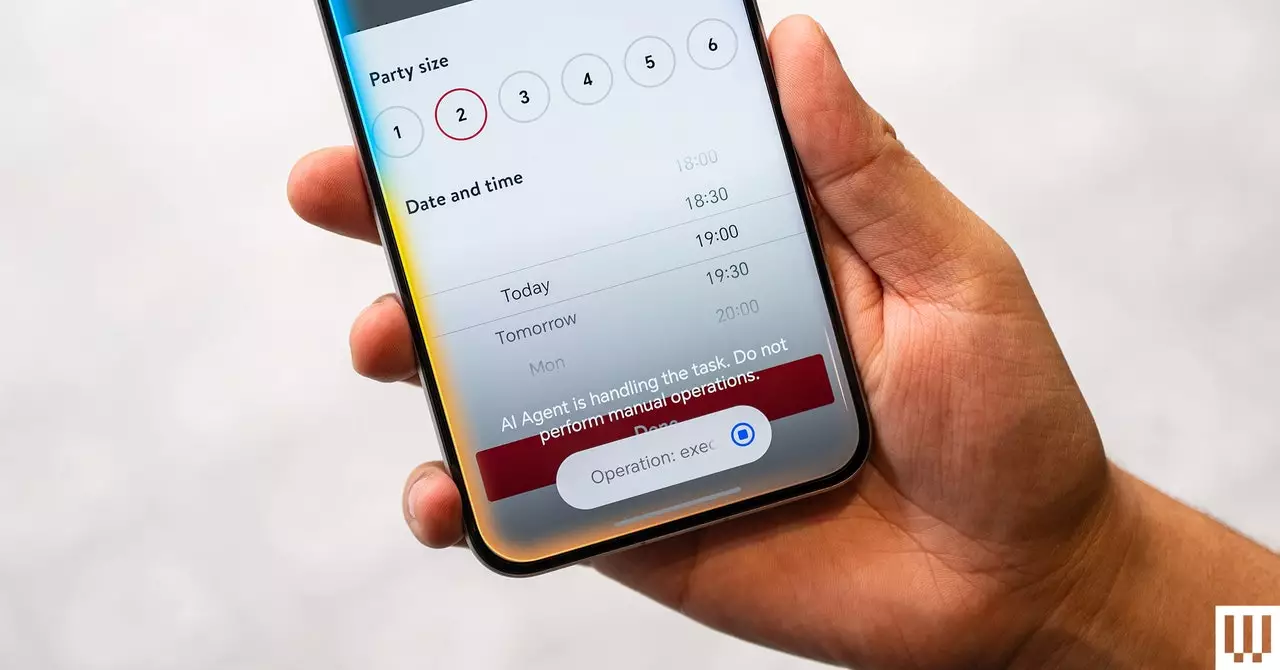
In today’s fast-paced digital world, the role of artificial intelligence (AI) in enhancing user experiences has garnered significant attention. One of the latest trends is the use of AI to streamline the process of making reservations at restaurants. However, while the concept sounds appealing, challenges persist that can hinder functionality and user satisfaction. For instance, an AI system may be capable of selecting a restaurant based on user input, but it often hits a snag when it comes to tasks requiring further validation, such as securing a reservation using credit card information.
The flexibility of AI systems shines through when users ask for “highly rated” establishments. By analyzing positive reviews, the system effectively narrows down options and curates a list of potential dining venues. However, this process can exhibit limitations, as the AI does not delve deeper into cross-referencing various online reviews nor does it tap into alternative reliable data sources. A fundamental reason lies in the architecture of these devices: much of the data processing occurs locally, meaning it doesn’t have access to cloud-based insights that could enhance decision-making. This raises questions about the depth and thoroughness of the AI’s analysis.
The emergence of so-called “agentic” AI has sparked conversations across the tech industry. This refers to AI systems designed to operate autonomously, completing tasks on behalf of users. A notable instance is Google’s Gemini 2 model, which can proactively manage online tasks based on user instructions. Such innovations bring forth the promising notion of a generative user interface, reflecting a significant shift from the traditional app-centric interactions that dominated previous generations of technology.
At trade shows like MWC 2024, numerous companies have showcased innovative approaches aimed at minimizing direct app interaction. Instead of navigating through individual applications, users can simply issue commands to AI assistants, allowing these systems to generate the necessary user interfaces dynamically. This is a departure from earlier methods, where applications’ APIs essentially dictated how services communicated with one another.
Honor’s approach to AI reservation assistance echoes techniques from the world of robotics and machine learning, emphasizing manual training for task completion. By allowing users to “train” their AI assistant—similar to Rabbit’s Teach Mode—the reliance on specific APIs is eliminated. Instead, the AI learns and remembers the processes involved, making future interactions smoother and more efficient. This method of “learning by doing” represents a critical leap toward more sophisticated AI systems capable of handling complex tasks with minimal direct user input.
The landscape of AI-driven reservation systems is rapidly evolving, with promising advancements on the horizon. Nonetheless, as these technologies continue to develop, it’s essential for developers and stakeholders to address existing challenges that impact user experiences. With ongoing improvement and refinement, the future of agentic AI holds the potential to transform ordinary tasks into seamless interactions, thereby enhancing how we engage with the digital world.

Leave a Reply