Whispering-gallery-mode (WGM) resonators, known for their ability to confine and concentrate light in a tiny circular path, have long been utilized in various high-resolution sensing applications. Traditionally used to detect chemical signatures, DNA strands, and single molecules, these resonators have shown great promise in fields such as biomedical diagnostics and environmental monitoring. However, the narrow dynamic range, limited resolution, and accuracy of WGM resonators have hindered their widespread use in the past.
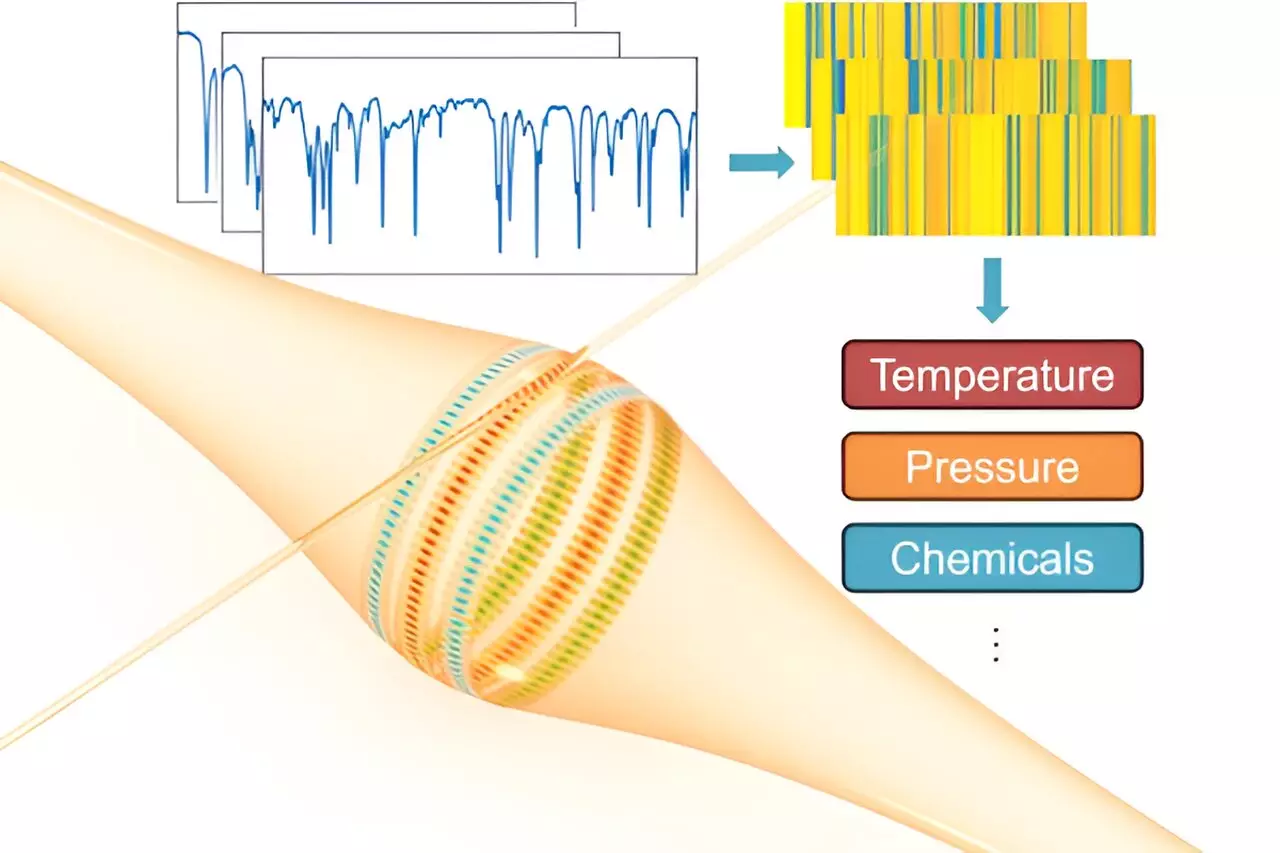
A recent study conducted by Lan Yang and Jie Liao from Washington University in St. Louis introduces a groundbreaking approach to enhance the capabilities of WGM resonators. By developing optical WGM barcodes for multimode sensing, the researchers have revolutionized the field of optical sensing technology. This innovative technique allows for the simultaneous monitoring of multiple resonant modes within a single WGM resonator, significantly expanding the range of measurements achievable.
The concept of multimode sensing enables researchers to pick up multiple resonance changes in wavelength, as opposed to just one, thereby increasing the sensitivity and accuracy of optical WGM sensing. By analyzing distinctive responses from each mode, the researchers were able to push the boundaries of WGM detection and estimate the sensing capabilities of a multimode system. Through their experiments, they found that multimode sensing could potentially offer a limitless range of measurements, surpassing the limitations of conventional single-mode sensing techniques.
Commercial Applications and Potential Benefits
The implications of these advancements in optical sensing technology are vast and far-reaching. In biomedical applications, researchers can now detect subtle changes in molecular interactions with unprecedented sensitivity, leading to improvements in disease diagnosis and drug discovery. Environmental monitoring can also benefit from multimode sensing, with the ability to detect minute changes in parameters such as temperature and pressure, enabling early warning systems for natural disasters and pollution monitoring in air and water.
One of the key advantages of multimode sensing is its potential for continuous monitoring of chemical reactions in real time. This capability opens up new possibilities for applications in pharmaceuticals, materials science, and the food industry. By leveraging the ultrahigh sensitivity of WGM resonators, researchers can now detect single particles and ions with great precision, paving the way for enhanced analysis and control of chemical processes.
The development of optical WGM barcodes for multimode sensing represents a significant advancement in the field of optical sensing technology. By overcoming the limitations of traditional single-mode sensing, researchers have unlocked new possibilities for high-resolution sensing applications in various industries. The potential for real-time analysis, continuous monitoring, and increased sensitivity offered by multimode sensing holds great promise for advancing research and innovation in the coming years.

Leave a Reply