In an era where privacy and data security are paramount concerns, social media giant Meta finds itself revisiting the contentious terrain of facial recognition technology. As it conducts trials involving facial matching processes aimed at curbing “celeb-bait” scams and enhancing user account security, the company must deftly manage a reputation marred by previous missteps.
One of the primary focuses of Meta’s renewed interest in facial recognition is the identification of fraudulent advertisements that exploit public figures’ images. By employing a facial matching process, Meta aims to thwart scams where malefactors leverage the likenesses of well-known personalities to bait unsuspecting users into engaging with deceptive advertisements that lead to illicit websites. According to the company’s statement, their systems will compare faces appearing in ads to the official profile pictures of high-profile users. If a match is found and the ad is identified as a scam, it is swiftly eradicated from the platform.
The implementation of this process illustrates a dual approach—aiming to protect users while reinforcing Meta’s commitment to improving advertising standards. However, the initiative raises questions about the efficacy of facial recognition in combating pervasive scam tactics. While such technological advancements offer potential solutions, they also introduce ethical dilemmas surrounding privacy and the extent of data surveillance.
Meta’s decision to re-enter the realm of facial recognition comes on the heels of a tumultuous history with the technology. The company faced mounting criticism from privacy advocates and civil rights groups, which led to the discontinuation of its facial recognition processes in 2021. This was part of a broader strategy to dissociate from a legacy characterized by user data misuse and scandals.
Despite officially shuttering its facial recognition operations, Meta remained aware of the growing applicability of such technology across various industries. For instance, in countries like China, facial recognition tools are employed to monitor public behavior, resulting in the tracking and penalizing of citizens for minor infractions, thus raising alarms regarding state surveillance.
As Meta cautiously reintroduces facial recognition features, it is clear that regulatory agencies in Western jurisdictions are closely scrutinizing these moves, wary of the power possessed by such technology in examining and categorizing individuals.
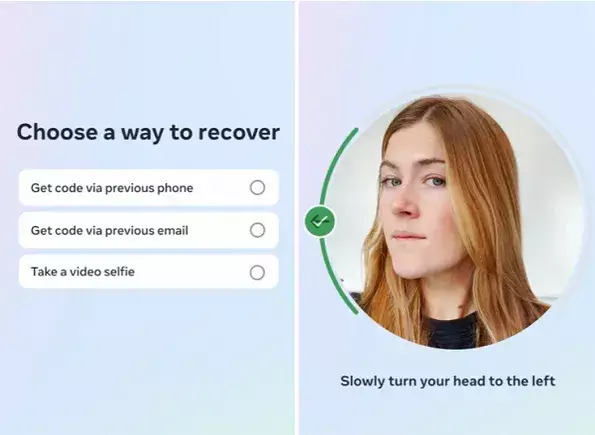
In addition to combating scams, Meta is testing the use of video selfies to facilitate identity verification during account recovery processes. Users will be asked to upload a video selfie, which will then be compared to their profile pictures utilizing facial recognition technology. This approach mirrors the security measures already found in various personal devices and applications. Advocating for user security, Meta emphasizes that the uploaded data will be encrypted and discarded post-verification, aiming to alleviate pervasive concerns about data retention.
However, this trial raises pertinent questions regarding the security of such practices. Although Meta insists that it will not retain users’ selfie data, the potential for misuse, even from the company’s end, cannot be overlooked. The conditioned acceptance of facial recognition as a security tool cultivates an environment in which privacy may increasingly yield to perceived safety.
Meta’s current exploration of facial recognition technology is a tightrope walk between innovation and ethical responsibility. By leveraging the technology for short-term, targeted applications, the company aims to enhance user security and credibility. However, challenges lie ahead—not least of which is regaining the trust of a public deeply skeptical of data practices.
The significant responsibility of ensuring user privacy while implementing such systems may lead to future complications for Meta. Each test and trial will be met with scrutiny, prompting questions around data use policies and long-term implications of facial recognition. As the public becomes increasingly wary of surveillance capabilities, Meta must find a way to engage with advanced technologies without alienating users.
Meta is at a critical juncture as it cautiously re-engages with facial recognition technology. While the pursuit of enhanced fraud protection and authentication mechanisms is admirable, it must navigate the treacherous waters of perceptions surrounding privacy and safety.
Ultimately, the successful integration of facial recognition within Meta’s operational framework will depend not just on technological execution but also on transparent communication and the implementation of stringent safeguards. By placing user privacy at the forefront, Meta may just find a way to rehabilitate its relationship with the public and innovate responsibly within the tech landscape.

Leave a Reply