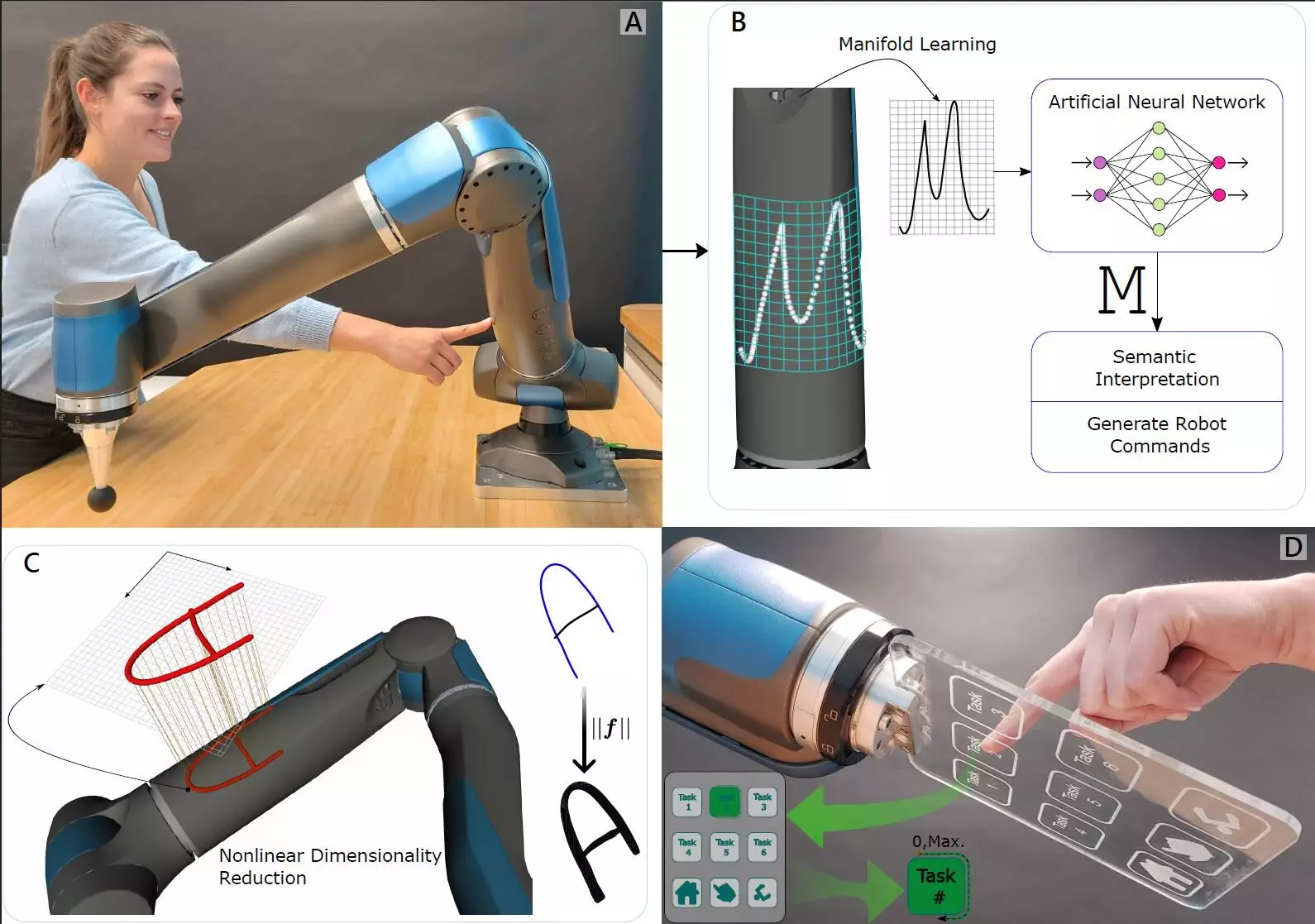
In a groundbreaking development, roboticists at the German Aerospace Center’s Institute of Robotics and Mechatronics are transforming the way robots perceive their environment. Their recent study in the journal Science Robotics unveils an innovative approach that shifts away from traditional artificial skin for touch detection. Instead, the researchers have ingeniously melded internal force-torque sensors with machine-learning algorithms, an integration that could redefine the capabilities of robotic interaction.
This novel method recognizes a fundamental distinction in touch—how living beings experience it on two levels: the sensation of touch and the reaction to being touched. Mimicking this dual experience in robots has always been a formidable challenge, primarily due to the complexities involved in replicating human tactile feedback systems. However, this research promises a significant leap forward, equipping robots with a more nuanced perception that could allow them to function more intelligently alongside humans.
Harnessing Torque for Sophisticated Sensory Feedback
At the core of this research is the strategic placement of ultra-sensitive force-torque sensors in the joints of a robot arm. These sensors are designed to measure the pressure applied from various angles, accurately sensing the dynamics of touch. For instance, elements such as torque provide crucial data regarding the applied force—akin to the sensations felt in our wrists when pressure is applied through our fingers. By capturing this intricate data, the robots can interpret their tactile interactions with precision previously unimaginable.
The integration of machine-learning technology elevates this sensation to new heights. By teaching the robot to recognize various types of tension and touch scenarios, the researchers enable more complex interactions. This advancement is exemplified by the robot’s ability to discern specific points along its arm being touched, showcasing its potential for selective sensitivity. This aspect of the research could lead to more refined and context-aware robot behaviors, enhancing their operational efficiency in environments requiring precise interactions.
Implications for Human-Robot Collaboration
This innovative approach not only enhances the sensory capabilities of robots but also paves the way for a new era of human-robot collaboration. In industrial settings, where robots often operate closely alongside human workers, the ability to perceive and respond to physical interactions is crucial. Robots can now engage in cooperative tasks with remarkable agility, adapting to the dynamics of human movement and touch.
The significance of this technology extends beyond industrial applications. It transforms our conceptualization of robotic interactions across various sectors, including healthcare, service industries, and even personal companionship. Robots equipped with this advanced touch-sensing technology could foster more meaningful interactions, enhancing the human experience while ensuring safety and efficiency in collaborative tasks.
As we move towards a future increasingly populated by intelligent machines, the implications of this research are profound. This pioneering work by the German Aerospace Center is not simply about robots that can feel; it is about creating machines that can genuinely understand and engage with their human counterparts. The journey towards intuitive robotics is ongoing, and this study marks a pivotal milestone in that evolutionary path.

Leave a Reply