Human-robot imitation learning has the potential to revolutionize the way robots interact with and assist humans in completing various tasks. The ability of robots to closely imitate human actions in real-time can lead to increased efficiency and adaptability in a wide range of scenarios. However, despite significant advancements in imitation learning techniques in recent years, there are still challenges that need to be addressed in order to fully realize the potential of this technology.
The New Deep Learning-Based Model
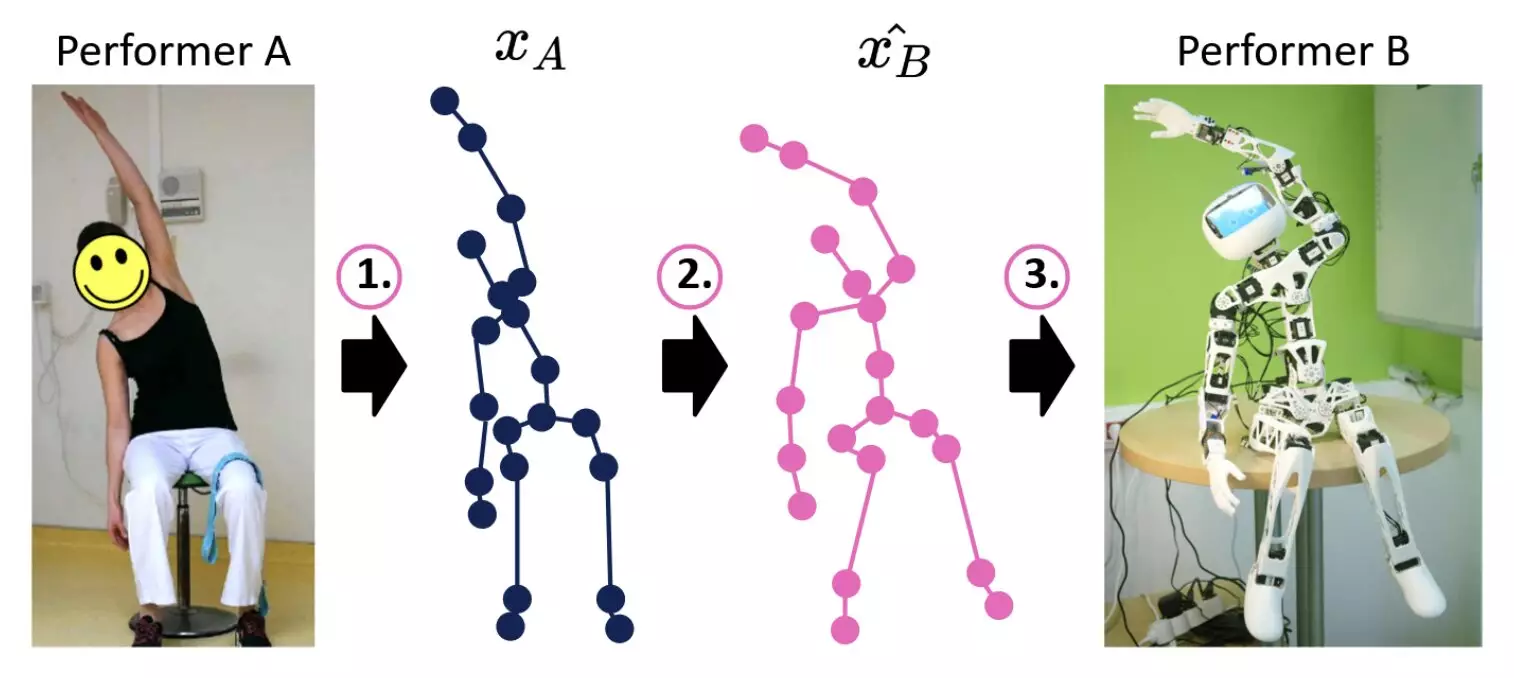
Researchers at U2IS, ENSTA Paris have introduced a new deep learning-based model aimed at improving the motion imitation capabilities of humanoid robotic systems. This model approaches motion imitation in three distinct steps, with the goal of reducing the discrepancies between a robot’s body and that of its human user. By translating sequences of joint positions from human motions to motions achievable by the robot, the model attempts to improve the online human-robot imitation process.
The Three Key Steps
The model developed by Annabi, Ma, and Nguyen breaks down the human-robot imitation process into three key steps: pose estimation, motion retargeting, and robot control. The use of pose estimation algorithms helps predict sequences of skeleton-joint positions based on human motions, which are then translated into joint positions realistic for the robot’s body. These translated sequences are then used to plan the robot’s movements, aiming to enhance its performance in completing tasks.
Despite the innovative approach taken by the researchers, the initial tests of the model did not yield the expected results. This suggests that current deep learning methods may not be sufficient for real-time motion retargeting. The researchers acknowledge the need for further experiments to identify and address potential issues with their approach in order to enhance the model’s performance.
The team recognizes the limitations of unsupervised deep learning techniques in enabling effective human-robot imitation learning. Their future work will focus on investigating the shortcomings of the current method, creating datasets of paired motion data, and refining the model architecture to improve retargeting predictions. By addressing these challenges and making necessary adjustments, the researchers aim to enhance the capabilities of robots in imitating human actions accurately and efficiently.
While human-robot imitation learning holds great promise for enhancing the capabilities of robotic systems, there are still significant challenges that need to be overcome. The development of innovative deep learning-based models, such as the one proposed by Annabi, Ma, and Nguyen, represents a step forward in addressing these challenges. By continuing to explore new approaches and refine existing techniques, researchers can unlock the full potential of human-robot imitation learning and pave the way for more advanced and versatile robotic systems in the future.

Leave a Reply