The field of quantum physics has been fascinating researchers for decades, with new discoveries being made frequently. Recently, scientists at the University of Bonn have made a groundbreaking discovery by manipulating light particles into a super photon, known as Bose-Einstein condensate. This innovative technique involves using tiny nano molds to shape the light into a lattice structure, paving the way for secure communication between multiple participants.
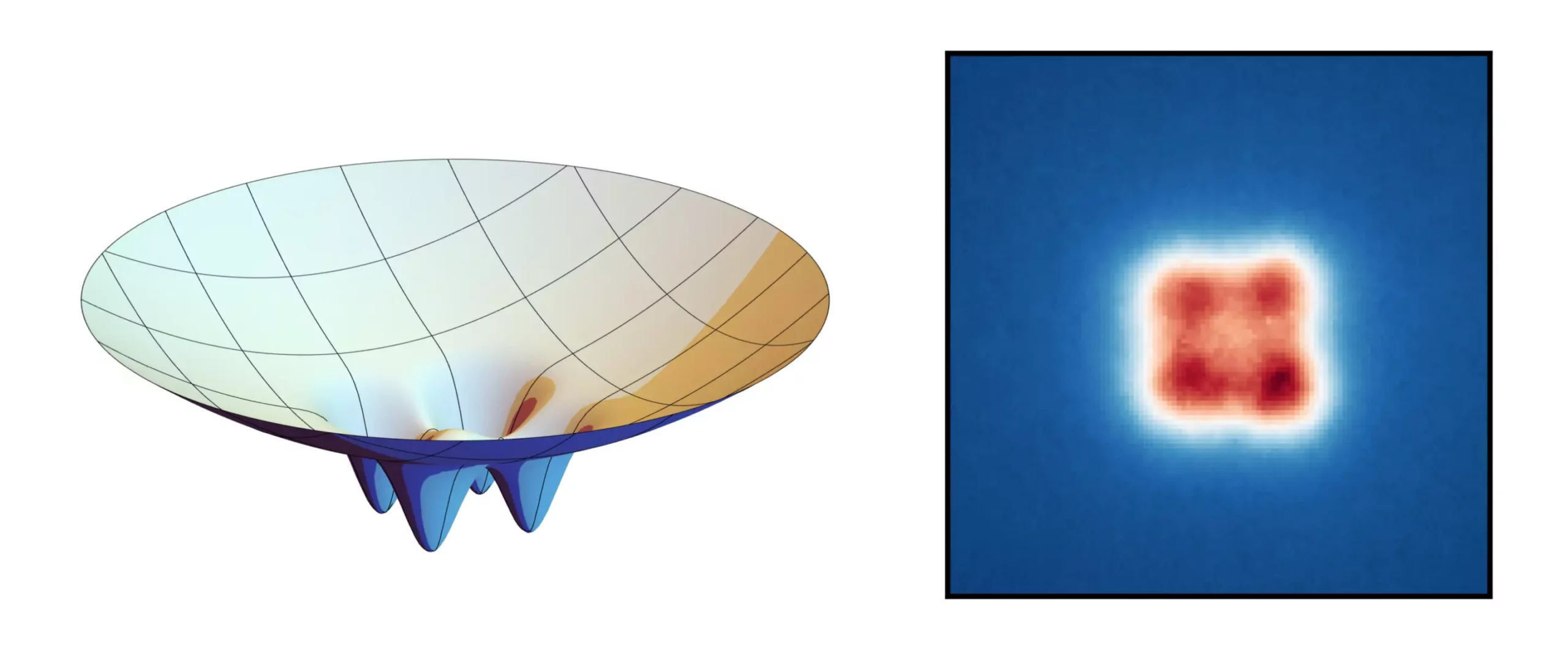
To create super photons, researchers fill a container with a dye solution and use a laser to excite the dye molecules, resulting in the production of photons. These photons bounce back and forth between reflective surfaces in the container, gradually cooling down until they condense into a super photon. By adding small indents to the reflective surfaces, researchers were able to imprint a lattice structure onto the condensate, similar to pressing a mold into sand.
The lattice structure created on the condensate allows for the manipulation of the super photons in a way that can enable quantum entanglement. This phenomenon, where the state of one photon affects the state of another, has significant implications for secure communication. By dividing the condensate into multiple regions while allowing for quantum mechanical interaction between them, it becomes possible to create a tap-proof method of exchanging information.
The potential applications of this technology are vast, with the ability to create Bose-Einstein condensates split between numerous lattice sites. This opens up the possibility of making communication between multiple participants secure, whether it is for discussions or secret transactions. By changing the form of the reflective surfaces, researchers can control the emission patterns of the super photons, tailoring them for specific applications.
The research conducted at the University of Bonn has opened up new possibilities in the field of quantum physics, particularly in the manipulation of super photons for secure communication. By imprinting lattice structures onto Bose-Einstein condensates, researchers have demonstrated a novel approach to creating tap-proof information exchange methods. As this technology continues to advance, it is likely to have far-reaching implications for various industries, from telecommunications to cybersecurity.

Leave a Reply