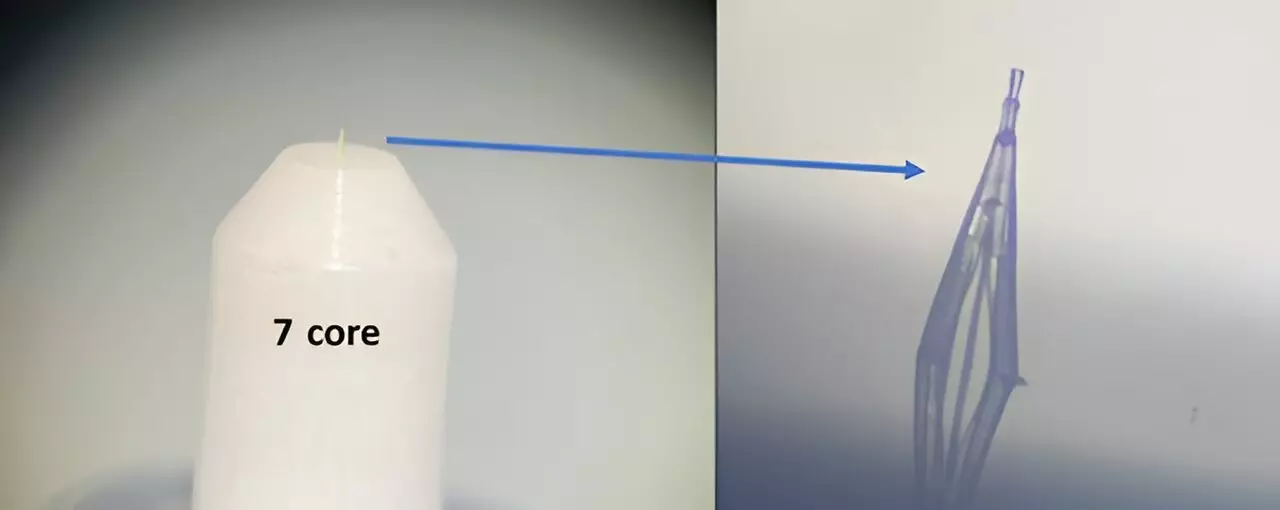
Advancements in photonic technology have paved the way for innovations in imaging, communication, and directed energy. One such breakthrough is the development of a free-standing microscale photonic lantern spatial mode (de-)multiplexer using 3D nanoprinting. This compact and versatile device marks a significant step forward in the field, offering new opportunities for system integration and the adoption of spatial multiplexing technology in various high-capacity communication systems and imaging modalities.
Unlike traditional systems that perform wavefront manipulations, the newly developed photonic lantern is characterized by its compact size and minimal footprint. These features make it far more accessible for integration into different technological contexts, offering a level of versatility that was previously limited by bulkier systems. The ability to directly print and adhere the device onto photonic circuits, optical fibers, and optoelectronic elements such as lasers and photodetectors further enhances its potential for widespread adoption.
The compact spatial mode (de-)multiplexer holds great promise for enabling space division multiplexing (SDM) in future high-capacity optical communication networks. By converting between optical waves containing a superposition of modes and an array of separated single-mode optical signals, this technology opens up new possibilities for enhancing the efficiency and capacity of communication systems. The device’s low insertion loss and minimal wavelength sensitivity make it a valuable asset for optimizing optical network performance.
Through the use of 3D nanoprinting and high-index contrast waveguides, researchers have succeeded in creating a device that can be seamlessly integrated into a wide range of applications with fine accuracy and high fidelity. This level of adaptability sets the stage for the device to be implemented in diverse optical systems and imaging modalities. Its ability to convert between multiple single-mode inputs into a single multi-mode waveguide showcases the versatility and potential impact of this technology on future developments in the field of photonics.
The development of the free-standing microscale photonic lantern spatial mode (de-)multiplexer represents a significant advancement in the field of photonic technology. By offering a compact, versatile, and high-performance solution for spatial multiplexing, this device opens new doors for the integration of advanced optical technologies into various applications. With its potential to enhance communication systems, imaging modalities, and other optical wave manipulation processes, the future looks bright for the continued evolution of spatial mode (de-)multiplexing technology.

Leave a Reply