Wireless internet has become an integral part of our daily lives, serving as a crucial tool for various activities such as professional communication, web browsing, and entertainment streaming. However, the increasing demand for wireless internet access has led to a surge in power consumption, contributing to the rise of carbon emissions globally. As a result, there is a pressing need for future wireless networks to support the high computational requirements of modern applications and internet services, while also minimizing energy consumption.
One innovative solution that researchers have been exploring is visible light communication (VLC). This approach leverages visible light, transmitted through light-emitting diodes (LEDs) or other artificial light sources, to enable wireless communication in an efficient manner. Recently, a team of researchers from Central University, IIDM, and CU J&K in India introduced a new hybrid system that combines VLC with RF communication. Their proposed hybrid solution, outlined in a paper published in IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, aims to facilitate reliable communication in indoor environments with high data transmission rates while consuming less energy.
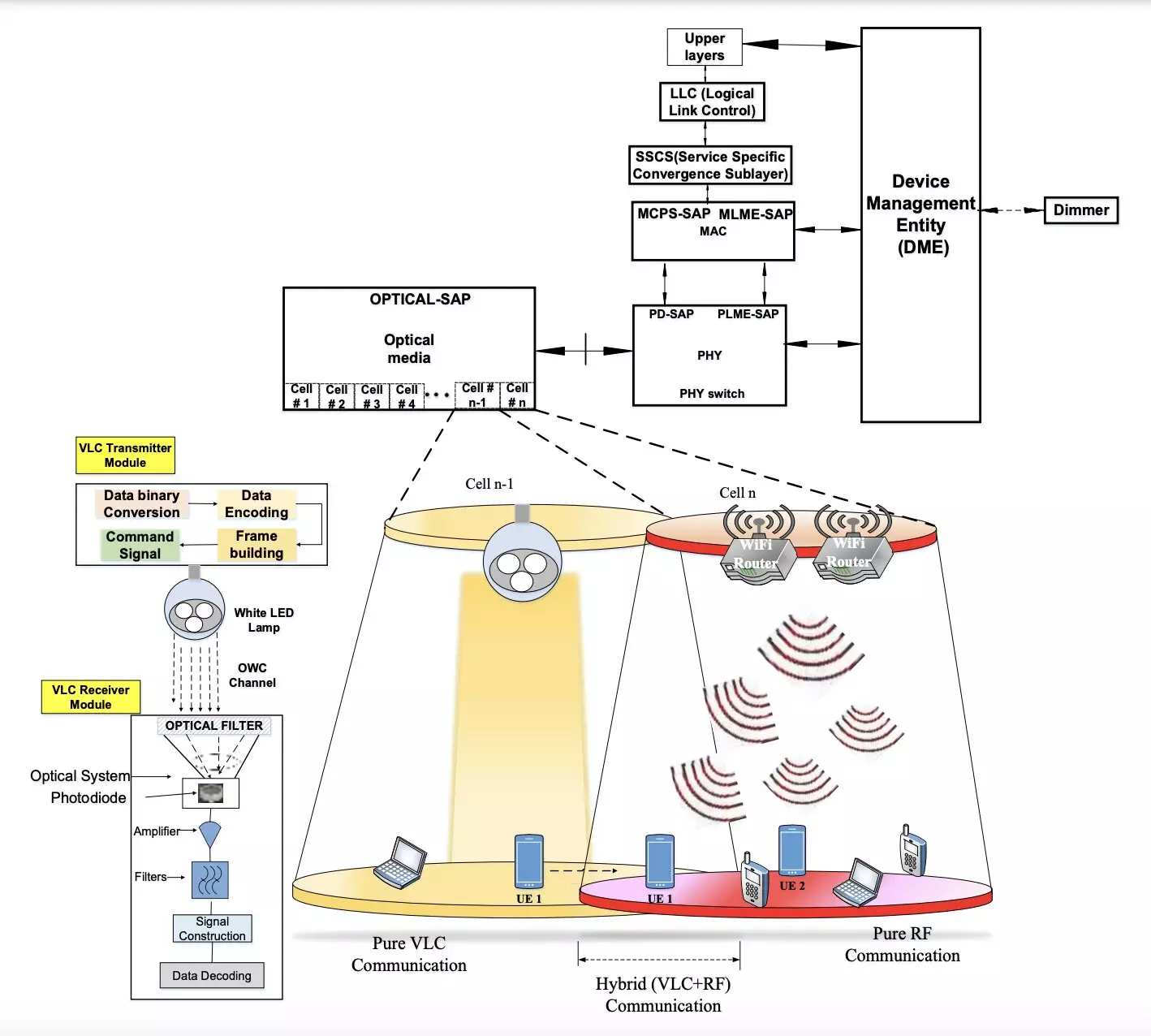
The Hybrid Communication System
The wireless communication system developed by the research team consists of two main components: a transmitter and a receiver module. These modules are physically separate but are connected via a VLC channel. The transmitter emits binary data in the form of LED-produced light, while the receiver, equipped with a photosensitive device such as a photodiode or camera, captures and extracts the transmitted information. The team suggests using modulation schemes to maintain a continuous data stream and ensure consistent power consumption during communication.
Evaluation of the Proposed System
To evaluate the performance of their indoor wireless communication system, the researchers conducted simulations using various platforms such as Python, Scilab, and MathWorks. Their findings indicate that the hybrid (RF+VLC) system demonstrates stable communication within the same indoor environment, resulting in significant energy savings. The team reported a high energy efficiency of approximately 37 low Specific Absorption Rate (SAR), lower incident and absorbed power density, reduced complexity, and temperature elevation in human body tissues exposed to radiation. Additionally, the proposed system was found to enhance the battery life of mobile devices by extending it by approximately 7 hours.
The study conducted by the research team contributes to the ongoing efforts to reduce power consumption and electromagnetic radiation in wireless communications. Their initial simulations showcase the potential of their approach in enhancing energy efficiency and improving communication reliability. Moving forward, further research and testing could refine and optimize the hybrid communication system, paving the way for more sustainable and reliable wireless networks in the future.

Leave a Reply