The recent collaboration between the Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology (SIAT) and Central China Normal University has led to a groundbreaking development in the field of medical imaging. A high-performance perovskite X-ray complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) detector has been created, promising to revolutionize the way we approach X-ray imaging for diagnostic and treatment purposes.
X-ray imaging plays a crucial role in diagnosing and treating cardiovascular and cancer diseases. While direct-conversion X-ray detectors made of semiconductor materials offer superior resolution and lower radiation doses compared to indirect-conversion detectors, they are not without limitations. Current semiconductor materials like Si, a-Se, and CdZnTe/CdTe have drawbacks such as low X-ray absorption efficiency and high costs, making them less than ideal for general X-ray imaging.
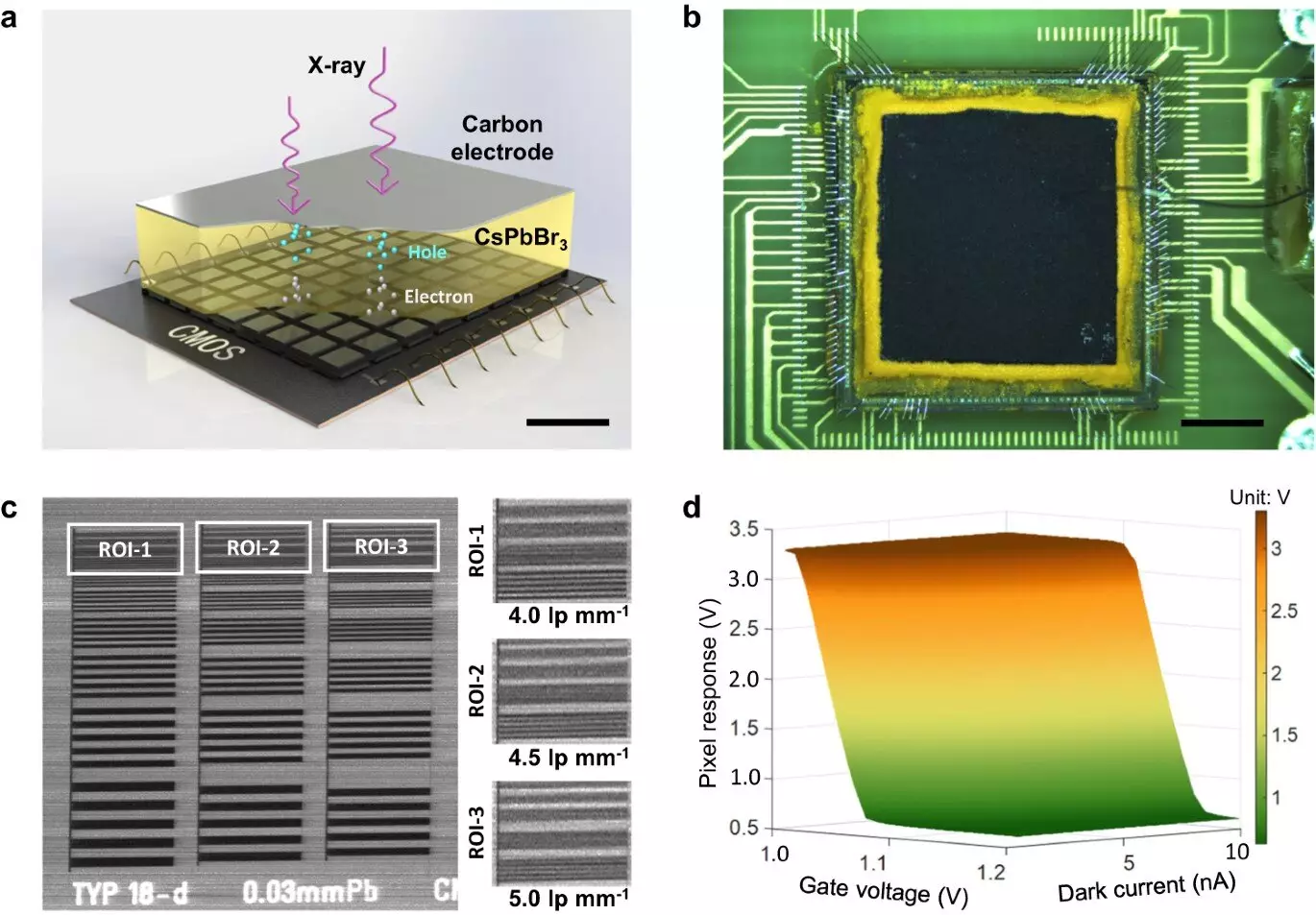
Perovskite has emerged as a promising alternative to traditional semiconductor materials due to its potential for high performance in X-ray imaging applications. However, the compatibility of perovskite with high-speed pixelated CMOS arrays was uncertain until now. The research conducted by SIAT and Central China Normal University has shown that a direct-conversion X-ray detector using a thick inorganic CsPbBr3 perovskite film on a dedicated CMOS pixel array can achieve remarkable results.
The experimental findings revealed that the thick CsPbBr3 perovskite film printed on the CMOS array demonstrated a high X-ray detection sensitivity, low dose detection limit, and impressive spatial resolution in 2D imaging. The proposed perovskite CMOS detector surpassed expectations with its ability to provide high-quality imaging at low radiation doses. Furthermore, the 3D CT imaging capabilities of the detector were validated at a rapid signal readout speed of 300 fps.
Prof. Ge, one of the lead researchers involved in the project, expressed optimism about the future of X-ray imaging with the use of lead halide perovskites. The development of state-of-the-art X-ray detectors with enhanced spatial resolution, readout speed, and low-dose detection efficiency has the potential to transform the field of medical imaging as we know it.
The collaboration between SIAT and Central China Normal University has paved the way for significant advancements in X-ray imaging technology. The innovative use of perovskite in combination with CMOS detectors has opened up new possibilities for improved diagnostic accuracy and reduced radiation exposure in medical settings. With further research and development, we can expect to see even more groundbreaking innovations in the field of medical imaging in the near future.

Leave a Reply