The development of flexible sensors with exotic sensing capabilities has been a significant advancement in the field of technology in recent years. However, the challenge lies in accurately measuring complex deformations resulting from forces or strains from multi-axes due to the Poisson’s effect of sensing materials, hindering the independent perception of biaxial stimuli.
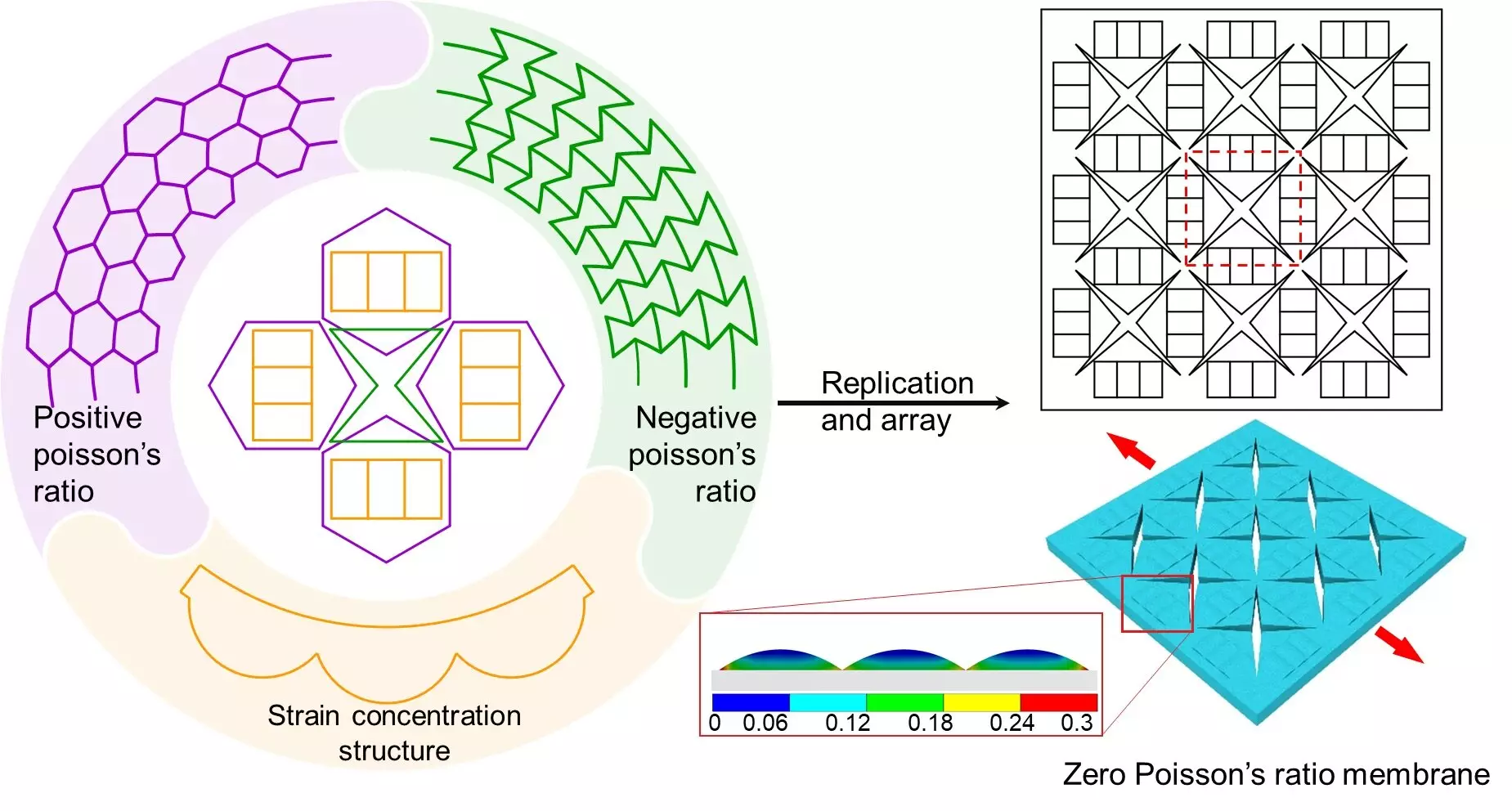
Researchers have identified zero Poisson’s ratio (ZPR) materials as a potential solution to the interference issues in biaxial or multi-axial stimuli perception. These materials maintain a constant transverse width under longitudinal strain, offering a promising approach to achieving independent perception of multi-axial stimuli.
The Study Led by Prof. Wu
Prof. Hao Wu and his student Dr. Xin Huang embarked on a study to explore the combination of traditional positive Poisson’s ratio (PPR) structures and negative Poisson’s ratio (NPR) structures to create a zero Poisson’s ratio structure. They discovered that the Poisson’s ratio of the hybrid structure could be adjusted by altering the feature size and width of the PPR and NPR structures.
Finite Element Analysis
Utilizing finite element analysis, the researchers determined the optimal parameters to obtain a zero Poisson’s ratio membrane. The PDMS membrane with the hybrid structure exhibited a significantly lower Poisson’s ratio of 0.07 compared to the PDMS membrane without the hybrid structure, which had a Poisson’s ratio of 0.43.
The flexible sensors based on ZPR membranes demonstrated the ability to accurately detect uniaxial and biaxial stimuli. When subjected to uniaxial stretching, the sensors exhibited a linear increase in electric resistance along the stretching direction, while the resistance perpendicular to the stretching direction remained relatively unchanged. This independent detection of biaxial stimuli enables the sensors to accurately measure force, strain, and motion status in complex deformation scenarios.
Enhanced Robotic Manipulation and Locomotion
The ZPR flexible sensors have shown great potential in enhancing robotic manipulation and locomotion. By accurately detecting contact forces between rigid manipulators and grasped objects, these sensors can provide crucial feedback for manipulation tasks. Additionally, the sensors can detect locomotion distance and direction in biaxial soft robots, contributing to improved performance and control.
Future Prospects
The exotic sensing capabilities of ZPR sensors hold promise for a wide range of applications in healthcare, human-machine interfaces, and robotic tactile sensing. With the ability to detect and respond to complex stimuli, these sensors are paving the way for innovative technological advancements in various fields.

Leave a Reply