Prof. Cao Xun and his research team at the Shanghai Institute of Ceramics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with experts from Huazhong University of Science and Technology, have unveiled a groundbreaking development in the realm of energy-saving windows. Their innovative electrochromic (EC) structure, as detailed in a recent publication in Nature Sustainability, represents a significant leap forward in the quest for sustainable building technologies.
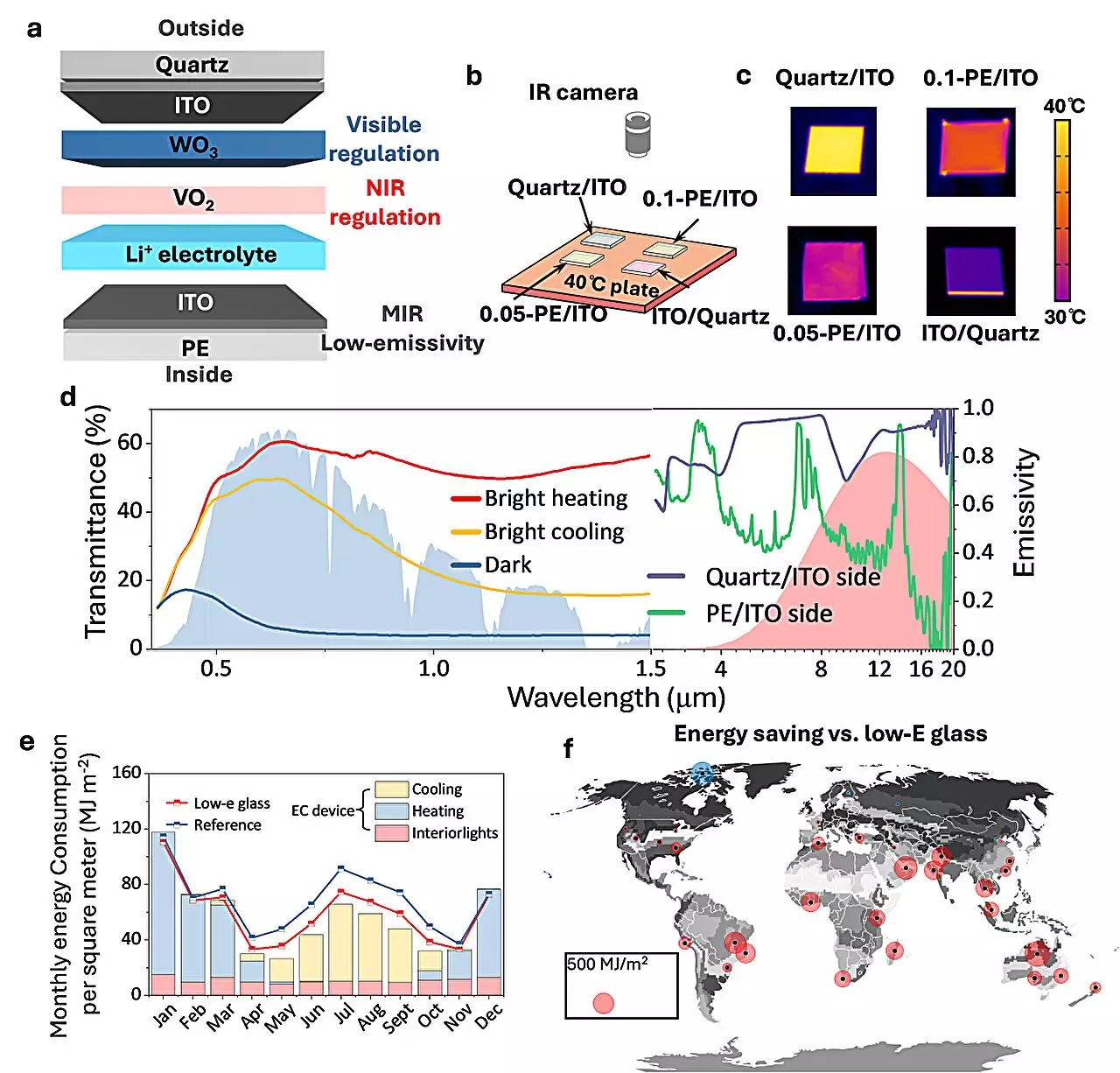
While traditional EC smart windows have shown promise in regulating solar radiation with external voltage, limitations persist, particularly in response speed and contrast ratio. Previous efforts have struggled to address the impact of solar radiation and outdoor temperature fluctuations. However, the team’s new design, featuring a VO2-WO3 tandem film and solid electrolyte, offers a solution by enabling the simultaneous control of solar heat and sunlight transmittance.
A key innovation lies in the structure’s ability to manipulate Li+ diffusion within VO2 and WO3, enabling independent regulation of near-infrared (NIR) and visible sunlight transmittance. Notably, VO2’s unique characteristics facilitate non-volatile state maintenance, setting it apart from WO3. This design element paves the way for enhanced energy efficiency in indoor lighting and heat exchange, marking a significant advancement in smart window technology.
Simulation studies underscore the superior performance of the new EC-based windows, showcasing notable heating and cooling energy savings compared to conventional low-E glass across diverse global climates. The team’s outdoor experiments in Sanya, Hainan Province, and Shanghai further validate the system’s effectiveness, demonstrating consistent cooling improvements ranging from 2°C to 14°C on clear sunny days.
The research team’s pioneering work in developing an advanced electrochromic smart window system heralds a new era of energy-efficient building solutions. By addressing long-standing challenges and introducing novel design features, these windows have the potential to revolutionize the way we approach sustainable architecture. With further refinements and real-world applications, the future looks bright for energy-saving windows and their transformative impact on the built environment.

Leave a Reply