Augmented reality (AR) stands at the intersection of the digital and physical realms, allowing users to engage with an enhanced view of the world around them. While many might initially associate AR with immersive video game experiences, its applications extend far beyond entertainment. In fields like surgery and autonomous driving, AR can provide precise and real-time information to enhance decision-making and operational efficiency. The ongoing evolution of AR technology promises to reshape how we interact with both digital content and our everyday environments.
One of the most significant challenges facing the AR industry revolves around the miniaturization and optimization of optical components. Traditional systems often rely on bulky designs that compromise portability and user experience. Current AR devices, such as head-mounted displays in gaming or automotive head-up displays, utilize complex multi-lens setups that, while effective, hinder widespread adoption due to their size and weight. Researchers and engineers continually search for innovative solutions that can effectively condense these systems without sacrificing quality.
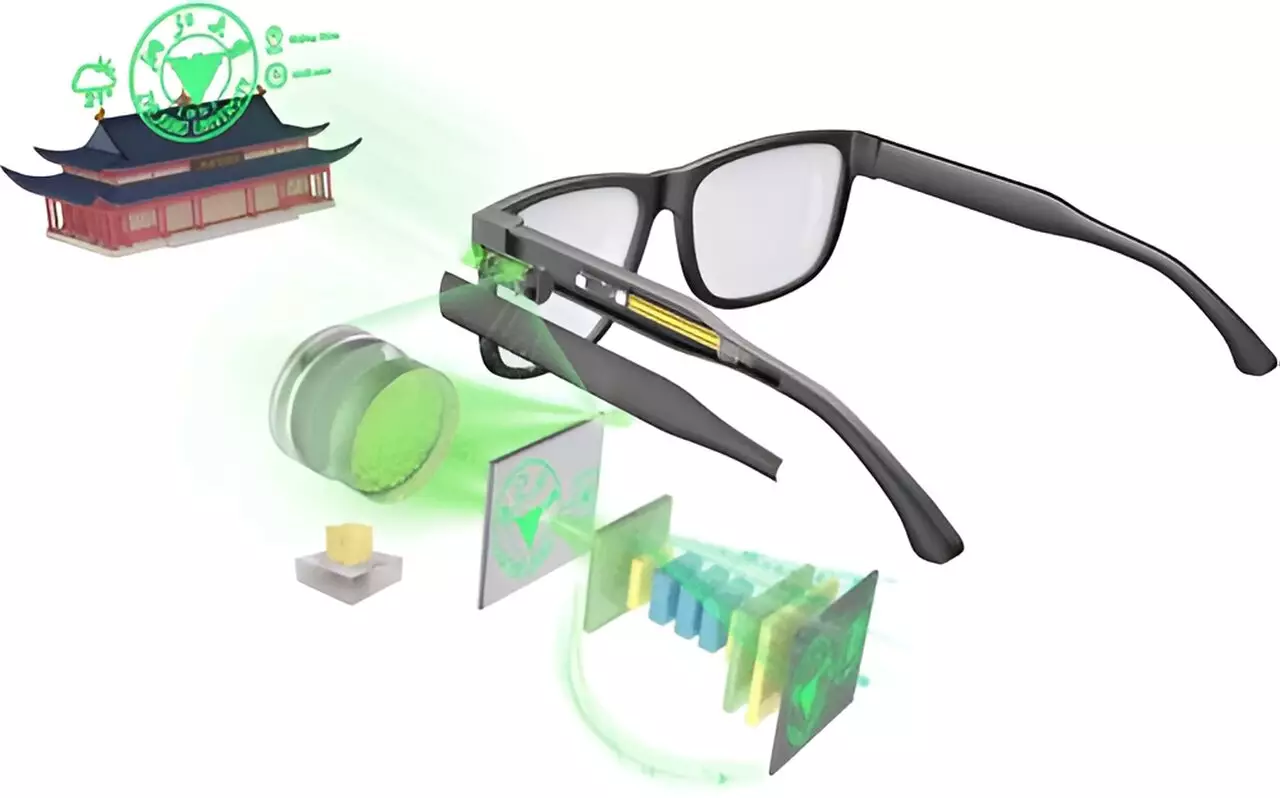
Recently, a promising advancement has emerged from the field of optical technologies. Researchers, led by Youguang Ma, have explored a hybrid approach that merges two distinct optical principles—metasurfaces and refractive lenses—alongside energy-efficient microLED screens. This innovative design allows for the creation of a compact, single-lens AR display specifically tailored for integration into ordinary eyeglasses. The metasurface—an ultra-thin film crafted from silicon nitride—is crucial in shaping and focusing the emitted light from microLEDs, which primarily oscillate in green frequencies.
Image quality represents a pivotal aspect of any AR device. To enhance the user experience, the research team implemented a sophisticated computer algorithm capable of detecting and correcting imperfections in the optical system. As the light exits the microLED setup, this algorithm minimizes distortions and maximizes resolution. With tests demonstrating the ability to achieve image quality on par with existing commercial AR systems, Ma’s prototype showcases less than 2% distortion even across a broad 30-degree field of view.
What does this mean for the future of AR technologies? The prototype not only demonstrated an impressive structural fidelity of 74.3% when comparing a reprojected image of a red panda to its original, but it also suggested the potential for transitions from monochromatic displays to full-color imagery. The implications are vast, as this technology could lead to the proliferation of lightweight, high-performance AR glasses that could seamlessly integrate into daily life. As researchers continue to refine and develop this platform, we may soon see AR systems that enhance our interaction with the world in groundbreaking ways.
The advancements in AR technology herald a new era, where everyday devices may soon transform into sophisticated interfaces blending digital information with real-world environments. With continued innovation in Optical Technology, researchers aim to create AR experiences that are not only highly functional and effective but also accessible to the average consumer, paving the way for an immersive future.

Leave a Reply