The development of robots for maintenance tasks has shown great promise in recent years. Engineers have successfully created a variety of robots designed to help maintain and repair infrastructure. However, many of these robots are limited by the need for external power sources. The Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems, Harbin Institute of Technology, and Hong Kong University of Science and Technology have collaborated to develop a new wireless miniature robot that can navigate through pipes and other tubular structures without the need for external power sources.
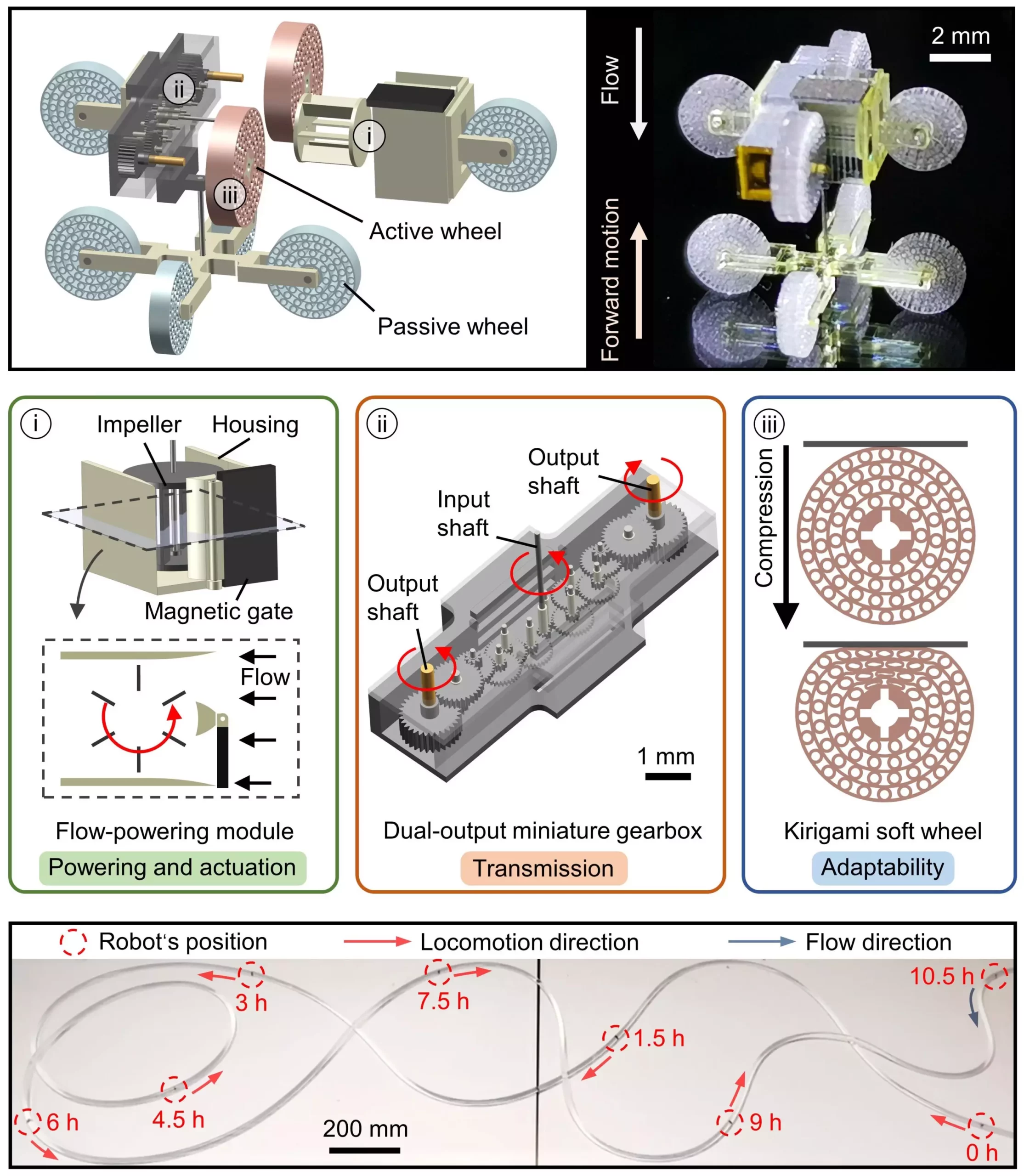
The wireless millirobot created by this team of researchers incorporates several key components that set it apart from previous maintenance robots. The robot includes a flow-powering module that converts fluid flow into mechanical energy, a dual-output miniature gearbox for efficient transmission of energy, and kirigami soft wheels for adaptive locomotion in complex tubes. This innovative design allows the robot to navigate through tubular structures with ease and perform maintenance tasks for extended periods of time without the need for external power sources.
One of the major advantages of this wireless millirobot is its ability to cover longer distances within tubular structures. The robot’s internal impeller converts fluid flow into mechanical energy, enabling it to move through pipes and other structures with ease. Additionally, the robot can modulate its direction of movement by simply applying an external magnetic force. These capabilities make the robot ideal for applications that require long-distance navigation and prolonged operation within confined spaces filled with flowing liquids or gases.
The researchers conducted preliminary tests to evaluate the performance of the wireless millirobot and found promising results. In future studies, they plan to further enhance the robot’s capabilities and stability to prepare it for real-world deployment. One area of focus for future improvements is increasing the robot’s ability to navigate in tubes with high flow rates or low-friction surfaces. Strategies such as streamlining the robot body to reduce flow resistance or adding microstructures to the wheel surfaces to increase friction could improve the robot’s performance in challenging environments.
The development of wireless millirobots for infrastructure maintenance represents a significant advancement in the field of robotics. These robots have the potential to revolutionize maintenance tasks in industries such as nuclear, industrial, and medical applications. By eliminating the need for external power sources, these robots can operate for extended periods of time and cover longer distances within tubular structures. With continued research and development, the future looks promising for the use of wireless millirobots in maintenance and repair tasks.

Leave a Reply