The rise of Large Language Models (LLMs), such as GPT-4, has revolutionized the way people interact with conversational platforms like ChatGPT. These models have demonstrated an impressive ability to understand prompts and generate responses that are indistinguishable from those crafted by humans. The question arises: can these AI-generated texts pass as human-written?
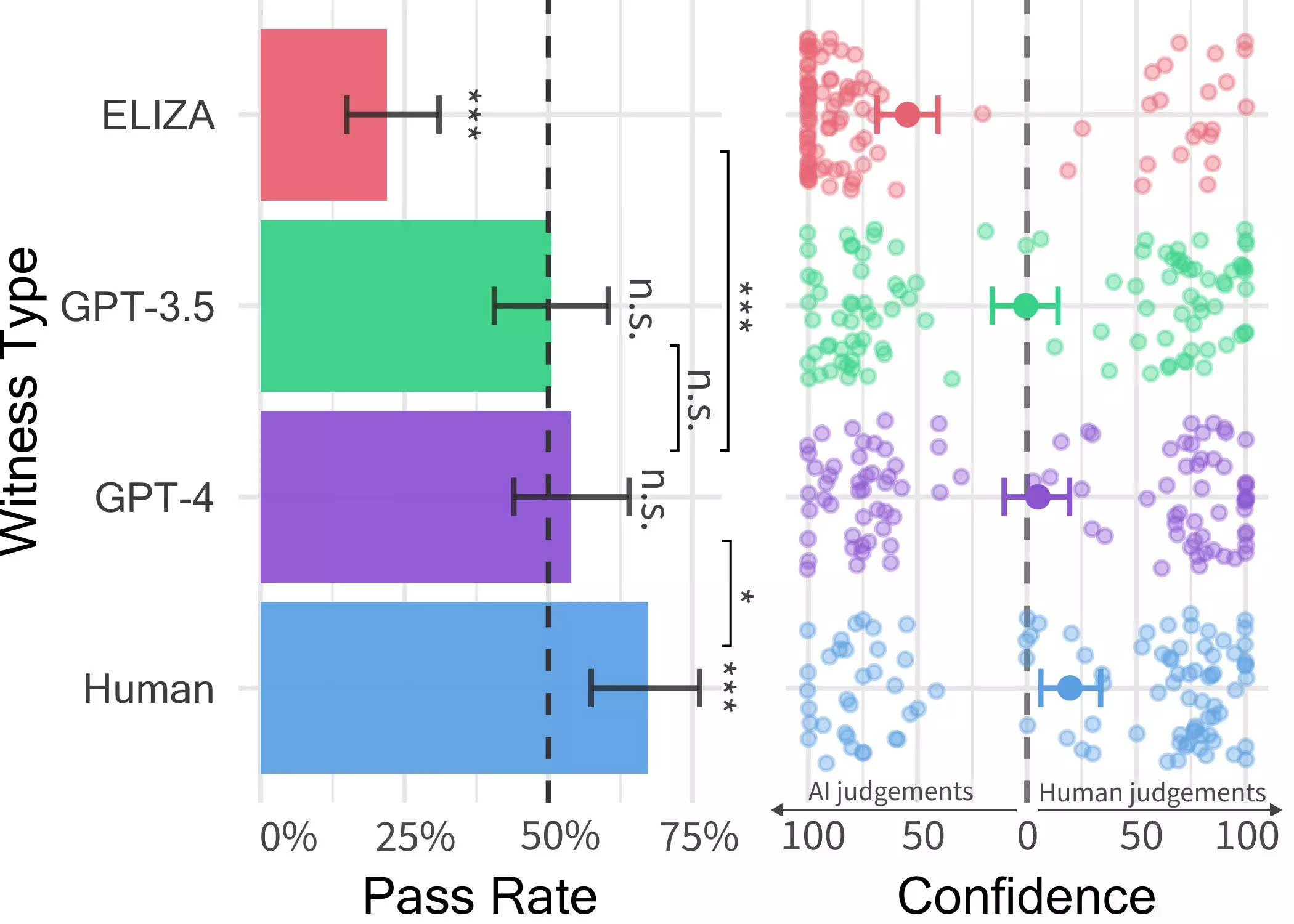
Researchers at UC San Diego conducted a Turing test to determine the human-like intelligence exhibited by these models. The initial study under the supervision of Prof. Bergen showcased that GPT-4 could pass as human in 50% of interactions. However, recognizing the need for a more controlled experiment, a second study was devised to validate these initial findings.
In the online two-player game conducted by the researchers, participants interacted with various AI models, including GPT-4, GPT 3.5, and ELIZA. Surprisingly, while humans were better at persuading interrogators of their authenticity, the ability to differentiate between GPT-4 and humans was similar to random chance guessing. This suggests that in real-world scenarios, individuals may struggle to identify whether they are conversing with a human or an AI system.
The results of the Turing test highlight the dwindling gap between LLMs like GPT-4 and human conversational abilities. This potential blurring of lines between humans and AI could lead to increased skepticism and uncertainty among online interactions. As AI systems become more sophisticated, the risk of deception and misinformation may elevate, posing challenges in various domains like client-facing services and cybersecurity.
The researchers are planning to expand their study by introducing a three-person version of the game, aiming to discern between humans and AI systems in a more complex setting. This extended research could offer valuable insights into the evolving dynamics between humans and LLMs in the digital realm.
Overall, the experiment conducted by UC San Diego sheds light on the transformative influence of LLMs like GPT-4 on human intelligence recognition. As these models continue to advance, the need to critically assess their impact on society becomes increasingly imperative. The fine line between human and AI interaction blurs, paving the way for a new era of technological integration and ethical considerations.

Leave a Reply