Plasma, often referred to as the fourth state of matter, is an ionized gas that contains electrons, ions, atoms, molecules, radicals, and photons. Unlike solids, liquids, and gases, plasma permeates everything and has ushered in a new era in technology. Previously, manufacturing electronic devices like mobile phones required the use of polluting chemical products to engrave circuits on silicon plates. However, the advent of plasma technology has revolutionized this process, enabling cleaner and more precise manufacturing, resulting in smaller and more advanced devices. This article explores the extensive applications of plasma, including its role in water treatment.
Plasma technology has transformed various industries, particularly electronics manufacturing. Historically, engraving circuits on silicon plates involved the use of harmful chemicals. The introduction of plasma technology has allowed for a cleaner and more precise process, making it possible to create smaller components. This breakthrough has revolutionized the development of mobile phones and other electronic devices, leading to advancements in communication and technology on a global scale.
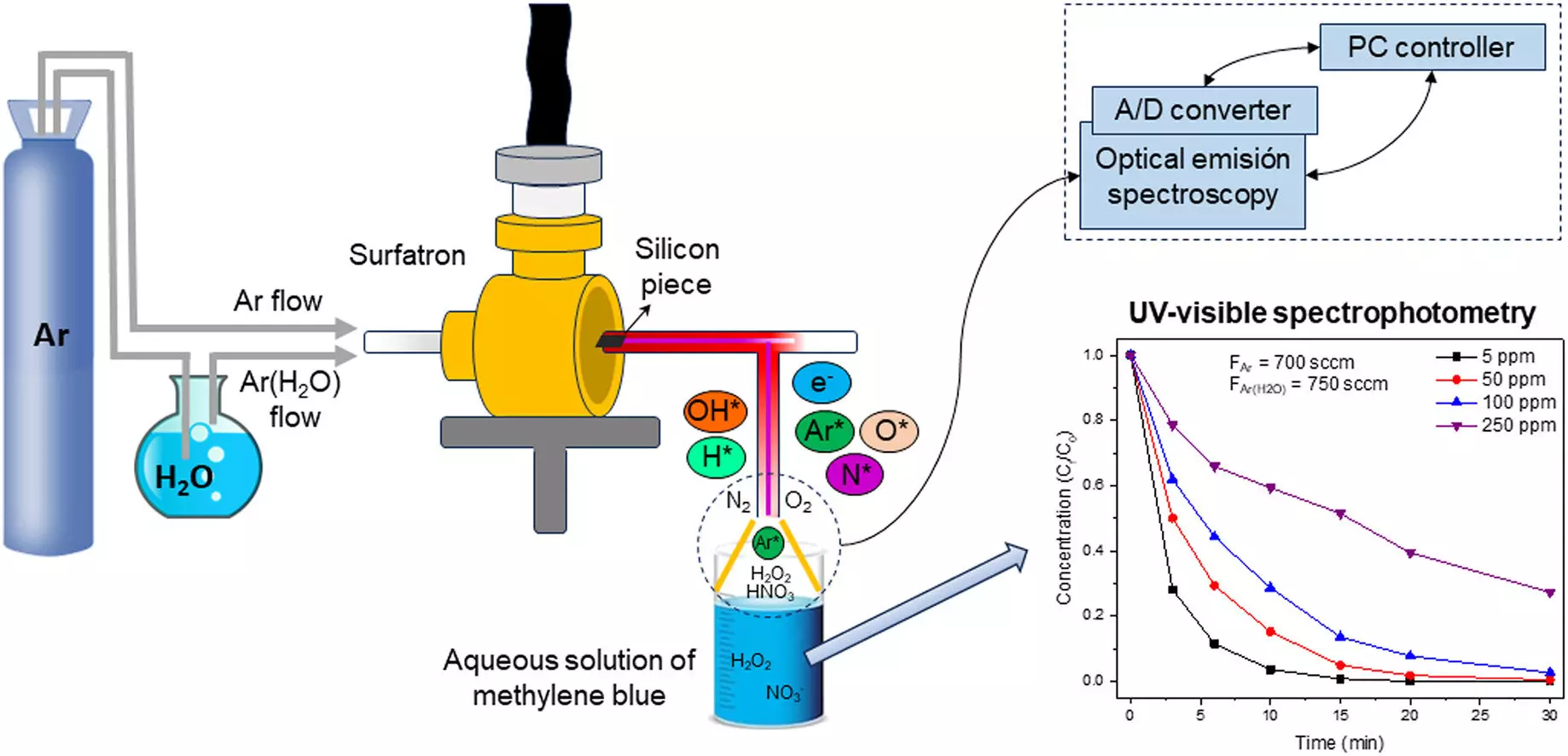
The Physics of Plasmas and Organic Catalysis and Nanostructured Materials groups at the University of Córdoba have conducted groundbreaking research on using plasma for water treatment. Their study, published in the journal Chemosphere, focuses on addressing the growing problem of organic pollutants in water, such as dyes and compounds from agricultural and industrial activities. By applying plasma to water, they have demonstrated the generation of reactive species containing oxygen and nitrogen. These species, including hydroxyl radicals and nitrogen radicals, have the ability to decontaminate water.
Enhancing Plasma Reactors for Water Remediation
Researchers Juan Amaro Gahete, Francisco J. Romero Salguero, and María C. García have made significant advancements in designing a plasma reactor that effectively generates these active species in water. By modifying the design of the surfatron, a metal device that mixes energy from a microwave generator with plasma, they achieved a more efficient generation of oxidizing species. This improved plasma reactor design enables the destruction of high concentrations of dyes, such as methylene blue, in just minutes. The addition of a small piece of silicon in the quartz discharge tube altered the plasma’s properties, resulting in a more effective and non-filamentary plasma.
The Mechanism: Reactive Species and Water Decontamination
When plasma components interact with water, they generate oxidizing species capable of degrading organic compounds and eliminating microorganisms. Described as a remote action, the plasma does not directly enter the water. Instead, it creates a zone of air between the plasma and water where numerous reactions occur. Collisions between excited species and molecules of oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor generate reactive species that diffuse into the liquid. These reactive species ultimately eliminate contaminants in the water. The researchers’ new plasma reactor design demonstrates remarkable potential for decontamination, achieving complete elimination of high concentrations of methylene blue dye in a short amount of time.
Expanding the Boundaries: Applications of Plasma
The innovative use of plasma technology extends beyond water treatment. With its ability to create active and reactive species, plasma finds applications in a wide range of fields. Plasma technology is being employed in manufacturing microchips, disinfecting surfaces, aiding in wound healing, depositing anti-reflective coatings on glasses, improving seed germination, recycling waste, activating the surface of plastics for better paint adhesion, and countless other applications. The versatility and effectiveness of plasma make it a powerful tool in various industries.
Plasma is reshaping technology and water treatment. Its ability to create active and reactive species renders it invaluable for numerous applications, from manufacturing advancements to environmental remediation. With ongoing research and innovative developments, plasma technology will continue to revolutionize various industries, offering cleaner, more precise, and more sustainable solutions. The power of plasma proves that the fourth state of matter is transformative and essential in our increasingly complex world.

Leave a Reply