A recent breakthrough in battery technology by researchers at Tohoku University has led to the development of a groundbreaking cathode material for rechargeable magnesium batteries (RMBs). This innovative material, with an enhanced rock-salt structure, has the potential to revolutionize energy storage solutions by providing a more cost-effective, safer, and higher-capacity alternative. The findings of this research were published in the Journal of Materials Chemistry A.
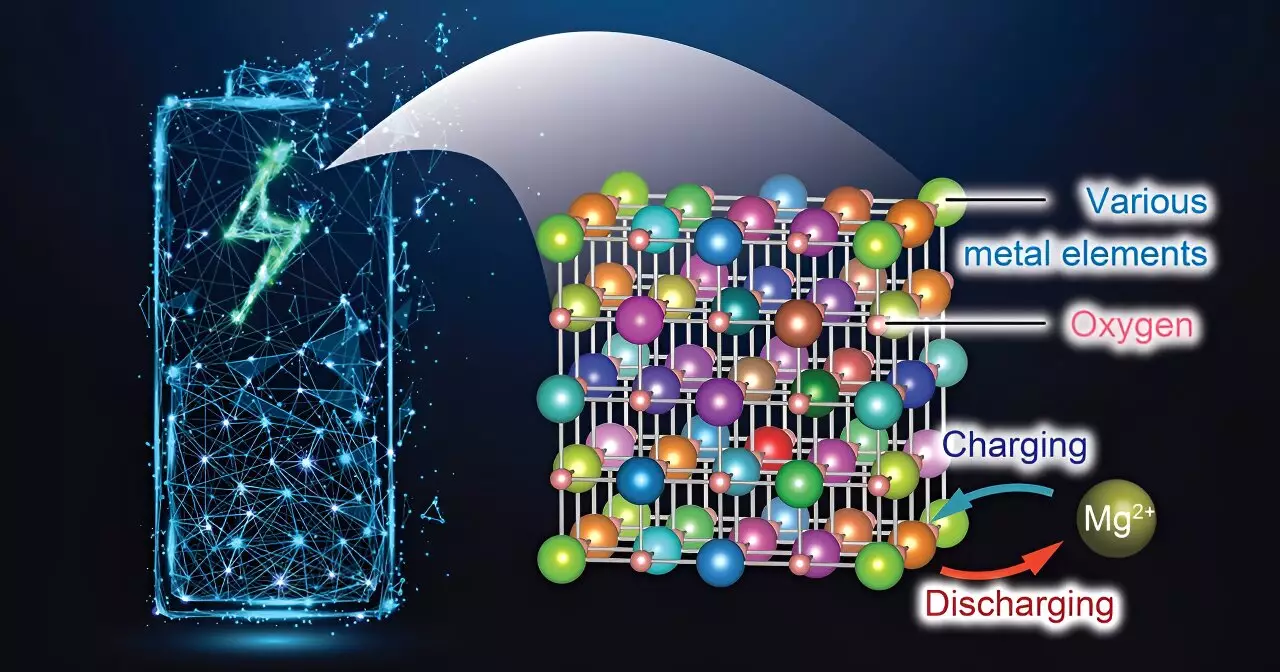
One of the key features of this new cathode material is the significant improvement in magnesium (Mg) diffusion within a rock-salt structure. The researchers were able to address the issue of Mg migration by introducing a strategic mixture of seven different metallic elements, resulting in a crystal structure with stable cation vacancies. This structural enhancement facilitates easier Mg insertion and extraction, marking the first use of rock-salt oxide as a cathode material for RMBs.
A major hurdle in the development of magnesium batteries has been the difficulty of Mg transport within solid materials, requiring high operating temperatures. However, the cathode material unveiled by the Tohoku University researchers operates efficiently at just 90°C, significantly lowering the required operating temperature and offering a more practical solution for energy storage.
Tomoya Kawaguchi, a professor at Tohoku University’s Institute for Materials Research (IMR), highlights the broader implications of this research. He notes that magnesium, being abundantly available, presents a more sustainable and cost-effective option compared to lithium. With the newly developed cathode material, magnesium batteries are expected to make significant contributions to grid storage, electric vehicles, and portable electronic devices, supporting the global transition towards renewable energy and reduced carbon footprints.
Collaborating with Kawaguchi, Tetsu Ichitsubo, also a professor at IMR, emphasizes the importance of harnessing the benefits of magnesium and overcoming previous material limitations. This research sets the stage for the next generation of batteries with significant impacts on technology, the environment, and society. Ultimately, this breakthrough represents a major step forward in the pursuit of efficient, eco-friendly energy storage solutions.

Leave a Reply